The Japanese Trademark Act stipulates that a trademark must contain distinctive features for its registration. Distinctiveness means that a certain trademark distinguishes the applicant’s goods or services from those of others. This article discusses an appeal against a JPO (Japanese Patent Office) Examiner’s Decision of Refusal of a trademark consisting solely of a very simple and common mark (Japanese Trademark Act, Article 3-1-5).
The present trademark was once rejected at the examination stage on the grounds that it lacks distinctiveness. However, at the appeal stage, it was determined that the trademark could play a function as a mark identifying the origin of the goods, and that it was not solely a very simple and common mark. Following an Appeal Decision of Grant, the trademark was ultimately registered.
Overview of the case
Appeal Number: Rejection 2025-005197
Date of Appeal Decision: August 14, 2025
Japanese Trademark Registration Number: 6967258
Date of Registration: September 12, 2025
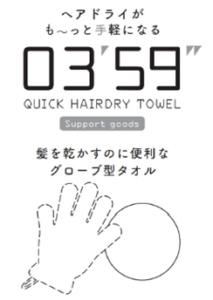
Present Trademark:
Related trademark registration numbers (Left: 6905735 Right: 6899030)
The present trademark is used for the above marks. The designated goods are in Class 24:
Articles of towel fabric; Towels of textile; Towel handkerchief; Towel cloth; Towel Comforter; Towel cover; Futon side of the towel; Towel pillow case; Cotton blanket; Towel sheet; Comforter made of towel fabric; Towel comforter; Chair covers of towel material; Wall Hanging Towel Fabric; Towel Material Table Hanger; Towel bedspread; Towel fabric; Towel fabric; Towel cloth; Kitchen towel made of towel fabric; Babies’ napkins of towel cloth; Table napkins of towel fabric; Toilet seat covers of towel material
(Excerpt from JPO https://www.j-platpat.inpit.go.jp/c1801/TR/JP-2023-121089/40/en)
Summary of Reasons for JPO Examiner’s Decision of Refusal
The present trademark displays the number 03’ 59”. Numerals are generally used extensively and categorically as symbols and signs to represent types, forms, and standards, etc. of goods (or the type, grade, etc. of services). In light of the above, it is appropriate to conclude that the present trademark is merely regarded as one consisting solely of a very simple and common mark and therefore, cannot be deemed to have distinctiveness to distinguish the goods thereof from others. Consequently, it falls under the rejection for failure to satisfy the trademark registration requirements (Japanese Trademark Act, Article 3-1-5).
Summary of Appeal Decision
The present trademark consists of the numerals “0359” written horizontally with a small right triangle positioned in the top right corner of 03 and two small right triangles positioned in the top right corner of 59. Within this composition, these right triangles can readily be understood as representing prime and double prime symbols. It is also widely known that a four-digit number in the form “○○’○○”” signifies “○○minutes ○○seconds” (where ○ represents any digit, and “ ’ ” and “ ” ” denote prime and double prime symbols, respectively).
Therefore, when the present trademark is used on the designated goods, it is natural to conclude that providers and consumers assume the present trademark displays the specific time “3 minutes 59 seconds” rather than recognizing symbols and signs for representing a product number, specification, or the like. In addition, despite the JPO conducting an ex officio investigation in the proceedings, no circumstances were found where combinations of four-digit numbers with prime and double prime symbols are generally used within the industry related to the goods.
Case History
- The Applicant filed a trademark application with the JPO on October 31, 2023
- The JPO issued a Notice of Reasons for Rejection on April 3, 2024
- The Applicant submitted Remarks to the JPO on May 16, 2024
- The JPO issued a Decision of Rejection on December 26, 2024
- The Applicant filed a request for Appeal with the JPO on April 4, 2025
- The JPO issued an Appeal Decision of Grant on August 14, 2025
Definition of very simple and common marks (Japanese Trademark Act, Article 3-1-5)
JPO Examination Guidelines for Trademarks, Chapter 7: Article 3(1)(v) (Very simple and common marks) all.pdf page 43
- “A very simple mark” is one whose composition is very simple.
- “Common mark”
What is “Common mark”?
– A mark commonly used as a symbol or mark indicating a product number, model number, type, form, specifications, etc. of goods or type, grade, etc. of services (hereinafter referred to as “symbols or marks of goods or services”).
– A figure commonly used as an outline
Examples of very simple and common marks (partial excerpts which could be informative to overseas applicants)
– numerals
– roman characters
a. Trademarks composed of one or two roman characters;
b. Trademarks composed of two roman characters combined with “-”
c. Trademarks to which one or two roman characters accompanied by “Co.,” “Ltd.,” or “K.K.” are attached. However, this is limited to cases where “Co.,” “Ltd.” or “K.K.” is judged to respectively mean “Company,” “Limited” or “Kabushiki Kaisha.”
– Combinations of Roman letters and numbers, for example, A2, AB2, 2A, A2B, 2A5
However, a trademark composed of the following structure is applicable only to a combination of roman characters and numerals generally used as symbols or marks of goods or services in a business which handles the designated goods or designated services:
Trademarks to which another roman character is added to the trademarks composed of one or two Roman characters followed by a numeral and trademarks composed of one Roman character to which another numeral is added to the trademarks composed of a numeral followed by one or two Roman characters.
– figures
– three-dimensional shape
– trademarks with a simple outline encircling characters