The EPO (European Patent Office) and IEA (International Energy Agency) released a joint study titled “Hydrogen patents for a clean energy future -A global trend analysis of innovation along hydrogen value chain-“ in January 2023. The voluminous 70 page report contains patent filing trends on hydrogen-related applications with analyzed by geographies, uses, and technical fields up until 2020. This article introduces a brief summary of the trends in Japan on the report and adds our own follow-up searches in 2021 and 2022.
What are the main tendencies of hydrogen patenting in Japan?
- Japanese applicants take a lead in hydrogen-related patents.
- This is because that trend is triggered by a close relationship with the automobile industry.
Why Japan takes a lead?
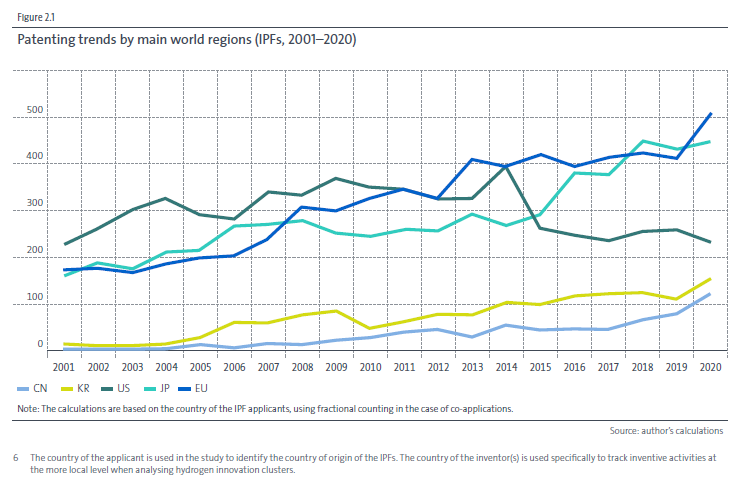
It is Japan and Europe that have continuously been boosting up the number of hydrogen patents since 2000. Japan achieved the highest growth rate in that field. Japan accounts for 20% of the number of published IPF cases, showing technical strength of all three main categories of hydrogen-related technologies: hydrogen production/storage, distribution, and transformation/industrial applications.
Fig. 2.1: International patenting trends in gaseous hydrogen storage, ammonia production, methanol production and alternative hydrogen-based fuels (IPFs, 2001-2020)
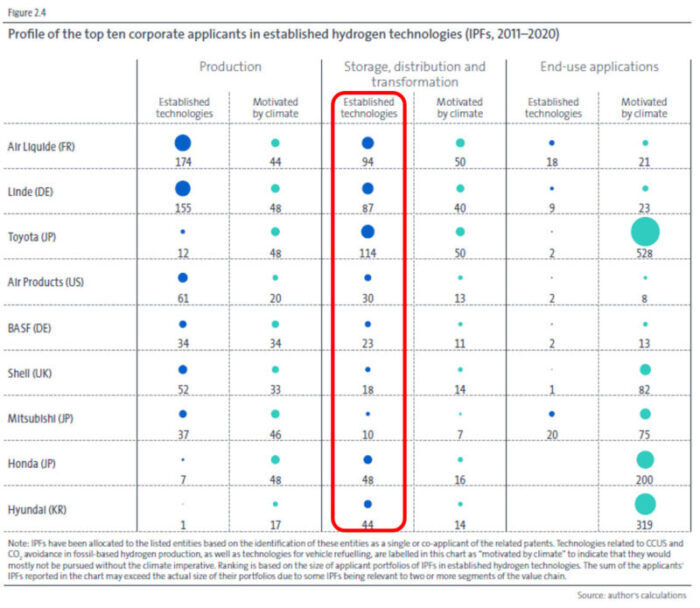
Emerging technologies motivated by climate change are Japan’s specialties. Patent applications related to those technologies are filed by automobile companies worldwide. Automobile companies are putting effort into fuel-cell vehicles apart from electric vehicles in a bid to mitigating environmental burdens. It seems that Japanese automobile industry’s competitive advantages have contributed to that strength. The trend also reflects the fact that three major manufacturers, Toyota (114 cases), Honda (48 cases), and Mitsubishi (10 cases), hold patents related to the storage, distribution and transformation of gaseous or liquid hydrogen.
Fig. 2.4 Profile of the top ten corporate applicants in established hydrogen technologies (IPFs, 2011-2020)
Taking a closer look at hydrogen production, European applicants account for 39% of all IPF cases. On the other hand, Japanese applicants account for 28% of IPF published in the field of electrolysis, showing its presence as a frontier of the development of electrolysis technologies. However, its practical application has yet to be established. Furthermore, as for hydrogen transformation, there are only a handful of its R&D players globally and more than half of applicants are universities and PROs. In the field of ammonia cracking, Japan accounts for a large share (61%) and eight out of ten top applicants in that field are Japanese. Toyota, Mitsubishi, and Hitachi are listed in the ranking.
Close link with the automobile industry
Since 2000, the number of automotive applications of hydrogen has become larger and continuously grows with more than 7% average annual growth rate in the past decade. As of the end of 2021, the number of global fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) ownerships reached 55,000 units, increased by 33,000 units from the previous year. Needless to say, this tendency backed a remarkable growth of FCEVs. In addition, existing technologies are mainly applied to cars and buses and are expected to be applied to trucks in the future.
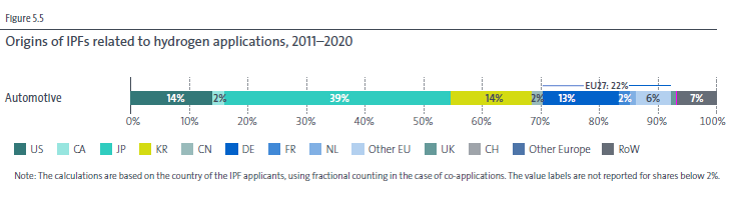
Japan is the top filer of automotive whereas the U.S. files most aviation applications, and Europe files ship applications. It indicates that each country will hone each specialty in the future. This joint report states that “Japan in particular shows a strong lead in hydrogen applications for the automotive sector – the most important sector in terms of patenting activities – .”
Our additional searches – patent filing trends in 2021 and 2022
In reference to the above EPO-IEA study featuring patent filing trends until 2020, our firm individually conducted additional searches to check whether the tendency until 2020 that are mentioned in the EPO-IEA report is followed by the same trend in 2021 and 2022. Our searches were conducted under same conditions of the above report. However, please be understood that the conditions are not completely same as the report.
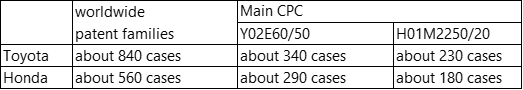
We conducted patent filing trends of Japanese companies, such as Toyota and Honda those who are gained attention in the report.
[Search conditions]
Filing year 2021 and 2022
Cases per patent family
Terminology any word including fuel cells
CPC definition in the above table is as follows:
Y02E60/50: TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE…Fuel cells;
H01M2250/20: ELECTRICITY…Fuel cells in motive systems, e.g. vehicle, ship, plane.
The trend shown in the above table has aligned with the analysis of the joint report which states that there are many applications motivated by climate change.
Summary
Every country is putting effort to develop climate mitigation technologies. For Japan, automobile makers are ramping up efforts on its technical development and filing patent applications related to hydrogen technologies. Triggered by the current circumstance led by automobile makers, it is hoping that the R&D of hydrogen-related technologies will become more active and be applied to other industries